Physical activity discusses all the movements we do throughout the day, such as doing housework and shopping, walking to work, and exercising, such as exercising or going to the gym. Evidence is mounting that physical activity benefits the body and mind and reduces the risk of many diseases. Here there are nine proven benefits of regular physical activity.

Table of Contents
1. It Helps Keep a Healthy Body Weight
Little physical activity increases the risk of becoming overweight or obese. Even though exercise alone does not necessarily result in weight loss, combined with a balance, calorie-controlled diet, it can contribute to successful weight loss. In addition, there is evidence that regular physical activity contributes to the long-term maintenance of a healthy body weight
2. It Lowers Blood Pressure-Physical Activity
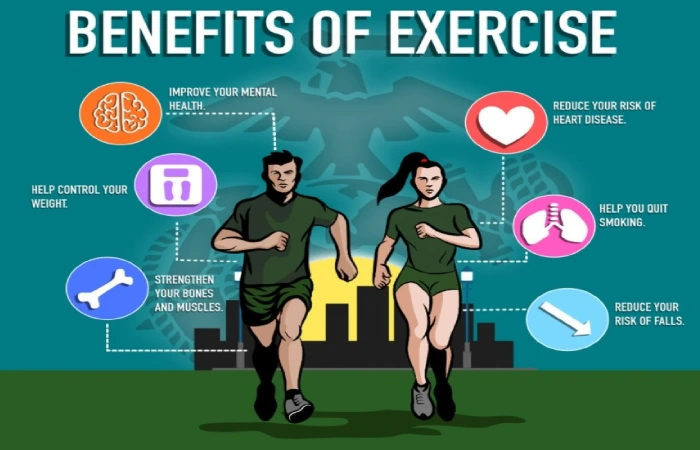
high blood pressure (or hypertension) is a hazard factor for many diseases, mainly stroke and heart disease. Regular physical activity can increase your heart strength, reducing the effort it takes to pump blood around the body. This decreases the pressure in the arteries, which leads to a reduction in blood pressure. There is moral evidence that regular physical activity helps maintain healthy blood pressure.
3. It Reduces the Risk of Heart Disease
Regular exercise, especially aerobic exercise like brisk walking, running, and cycling, has been shown to reduce the risk of developing heart disease. This benefit is seen in people of all sizes. Overweight or obese individuals who are physically active are much less likely to develop heart disease than inactive individuals.
4. It Lowers the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Exercising is known to help regulate blood sugar levels and improve our body’s insulin sensitivity. On the other hand, it has been shown that physical inactivity increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Regular exercises are also suggest for people with diabetes to help control their blood sugar levels.
5. It Reduces the Risk of Certain Types of Cancer
Cancer is a intricate disease influence by many manageable (e.g., smoking, unhealthy diet, excessive alcohol consumption) and uncontrollable (e.g., genetics, radiation, environmental pollutants) factors. Evidence suggests that regular, moderate to dynamic exercise can help reduce our risk of developing certain types of cancer, including colon, rectum, lung, and breast cancer.
6. It Increases Muscle Strength and Function
Skeletal muscle performs numerous functions – supporting posture, controlling movement, and generating body heat. As we age, our muscle mass typically decreases due to a more inactive lifestyle. This loss of muscle physique can reduce our mobility and increase our risk of falling and developing muscle diseases like sarcopenia. Exercising regularly, especially resistance training (like weightlifting or bodyweight exercises like squats and push-ups). Can help improve muscle strength and resistance and reduce our risk of muscle disorders like sarcopenia.
7. It Improves Bone Health and Strength
Bodyweight exercise (e.g., running, dancing) and resistance training have remain shown to improve bone density in adolescents and help maintain bone density in adulthood. Thereby reducing the risk of osteoporosis. This especially important for older adults and menopausal women because it slows the natural loss of bone density that occurs with age.
8. It Helps Promote Positive Mental Health-Physical Activity
Exercising regularly shown to impact our mental health and psychological well-being positively. The exact mechanism by which exercise benefits our mental health not fully understood. What known regular exercise supports the release of endorphins, helps reduce stress, and promotes healthy sleep patterns, all of which combine to improve our state of mind. Additionally, some evidence is that exercising may even help treat depression and other mental disorders.
9. It Reduces the Risk of Dementia
It shown that regular exercise protects against cognitive decline. although how exercise reduces cognitive decline not fully understood, and recent evidence suggests that the release of proteins known as neurotrophic factors plays important role.
These beneficial factors help promote the growth and repair of neurons, which helps support normal cognitive function. This may partially explain why older adults who remain active throughout life have a significantly lower risk of rising mental disorders such as dementia and Alzheimer’s.
Also Read: https://www.workpublishing.com/castor-oil/
Proven Benefits of Physical Activity
The World Health Organization recommends the following:
- We should do at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity per week. or at least 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical exercise per week, or the appropriate combination of moderate-intensity and vigorous-intensity activity.
- Aerobic activities should done in bouts of at least 10 minutes.
- For extra health benefits, adults should aim to increase their moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity to 300 minutes per week or 150 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical exercise per week. Or an equivalent combination of moderate-intensity and vigorous-intensity activity.
- Muscle strengthening anaerobic activity involving the major muscle groups (legs, hips, back, abdomen, chest, shoulders, and arms) should done at least two days per week.
People with previous health problems are advise to seek advice from a doctor before engaging in any additional activities.
Also Read: Burger – Camp Branch Photos

